As energy efficiency and sustainability become increasingly crucial, heat pumps have emerged as a leading solution for heating and cooling homes. But what makes them so efficient, and are they truly the future of heating? Let’s explore the science behind heat pumps and their potential to revolutionize the way we heat our homes.
How Do Heat Pumps Work?
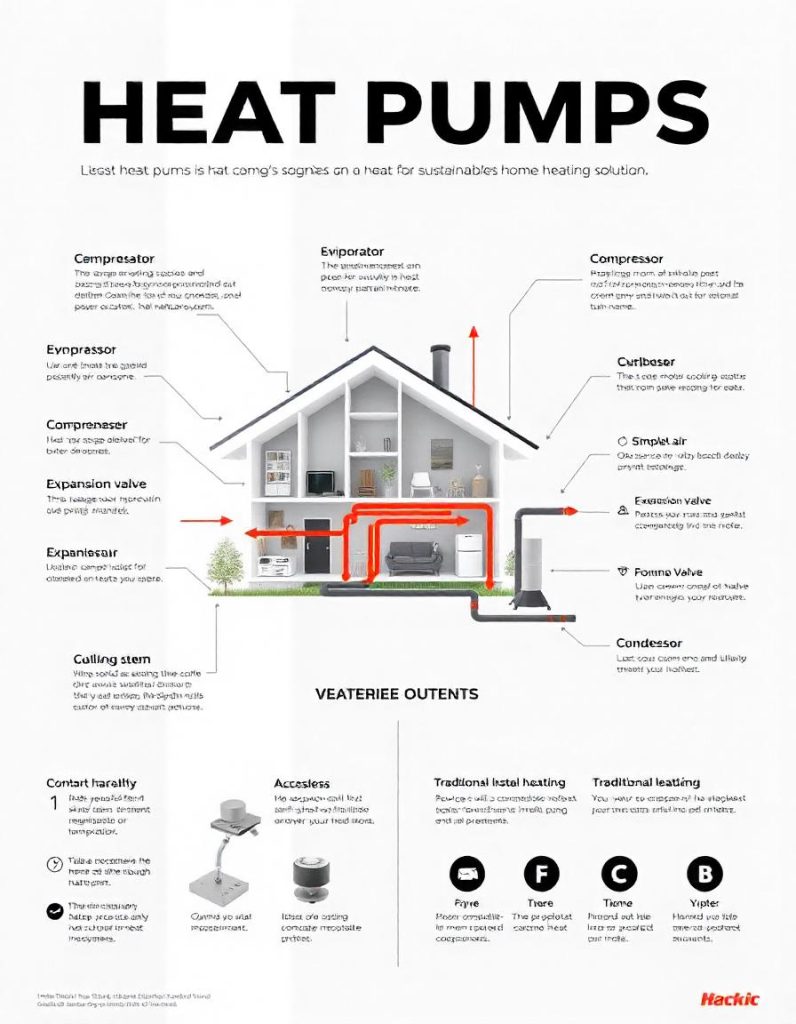
Unlike traditional heating systems that generate heat by burning fuel, heat pumps transfer heat from one place to another. They operate on the principle of thermodynamics, using refrigerant and a cycle of compression and expansion to extract heat from the air, ground, or water and move it indoors.
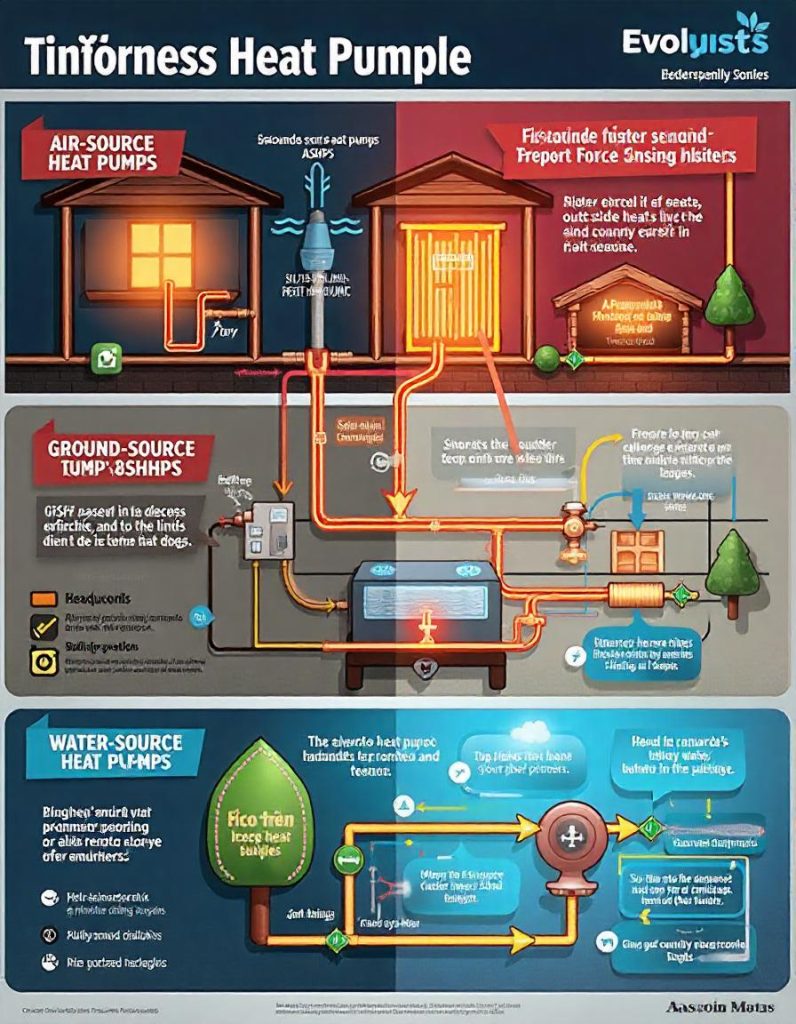
There are three main types of heat pumps:
- Air-source heat pumps (ASHPs): Extract heat from the outside air, even in cold temperatures, and transfer it indoors.
- Ground-source heat pumps (GSHPs): Also known as geothermal heat pumps, these systems extract heat from the ground, where temperatures remain more stable year-round.
- Water-source heat pumps: Use a nearby water body as a heat source or sink, making them ideal for locations with access to lakes, rivers, or wells.
The Science Behind Their Efficiency
Heat pumps are incredibly efficient because they move heat rather than generate it. Their efficiency is measured using the Coefficient of Performance (COP) and Seasonal Performance Factor (SPF). While traditional furnaces operate at 80-95% efficiency, meaning they convert nearly all the fuel into heat, heat pumps can achieve efficiencies of 300-400% because they transfer more energy than they consume.
In colder climates, heat pumps may require auxiliary heating sources, but advancements in technology, such as variable-speed compressors and improved refrigerants, have made modern models much more effective in sub-zero temperatures.
Benefits of Heat Pumps



- Energy Efficiency: By leveraging existing heat, they use significantly less energy than fossil fuel-based heating systems.
- Lower Carbon Footprint: Since they rely on electricity rather than combustion, heat pumps reduce greenhouse gas emissions, especially when powered by renewable energy.
- Cost Savings: While initial installation costs may be high, the long-term savings on energy bills often outweigh the upfront expense.
- Year-Round Comfort: Heat pumps provide both heating and cooling, eliminating the need for separate HVAC systems.
- Government Incentives: Many governments offer rebates and tax credits to encourage the adoption of heat pump technology.
Are Heat Pumps the Future of Heating?
As the world transitions towards sustainable energy solutions, heat pumps are increasingly recognized as a key player in the decarbonization of home heating. Their ability to operate efficiently in various climates, combined with advancements in heat pump technology, makes them a viable alternative to gas and oil-based systems.
Furthermore, with the push for electrification and the increasing adoption of renewable energy sources, heat pumps align perfectly with global efforts to reduce reliance on fossil fuels. Countries like the UK, Germany, and the U.S. are investing heavily in heat pump infrastructure, and industry trends indicate that heat pumps could become the dominant heating technology in the near future.

Conclusion
The science behind heat pumps highlights their remarkable efficiency and sustainability. With rising energy costs, stricter environmental regulations, and an increasing focus on renewable energy, heat pumps are poised to become the future of home heating. Homeowners and businesses alike stand to benefit from this innovative technology, making the shift to heat pumps a smart and eco-friendly choice.
If you’re considering a heat pump system, now may be the perfect time to invest in this energy-efficient solution and contribute to a greener future.
